- AME CAPITALS
- Trading Technology
- Help AME Trading
Chapter 6. Buying/Selling Rates and Spread
Up until now, when discussing quotations, we deliberately used only the current (spot) currency rates in order to simplify the understanding of the website's material. In reality, every quotation in Forex has two rates (two prices) - the buying rate (bid) and the selling rate (ask). These rates are usually denoted by a slash ("/"), where the buying rate is indicated before the slash, and the selling rate is indicated after the slash. For example, USD/JPY 104.75/104.85.
The buying rate refers to the price at which the party quoting the rate is willing to buy the base currency from you. The selling rate refers to the price at which the party quoting the rate is willing to sell the base currency to you. In other words, the concepts of buying and selling are "reversed" from your perspective. In this formulation, it is not you who is buying or selling, but rather the party offering the quotation. In simple terms, if you intend to buy the base currency of the quotation, you should look at the selling price (ask). If you intend to sell the base currency of the quotation, you should look at the buying price (bid).
For example, if you intend to purchase 100 US dollars with Japanese Yen at a USD/JPY quotation of 104.75/104.85, you will need 100 x 104.85 = 10,485 Japanese Yen. On the other hand, if you intend to acquire Japanese Yen by selling 100 US dollars, you will receive 100 x 104.75 = 10,475 Japanese Yen.
Depending on the trading platform provided by internet brokers to their clients, the graphical representation of quotations may vary. An example of a graphical display of quotations is shown in the figure.
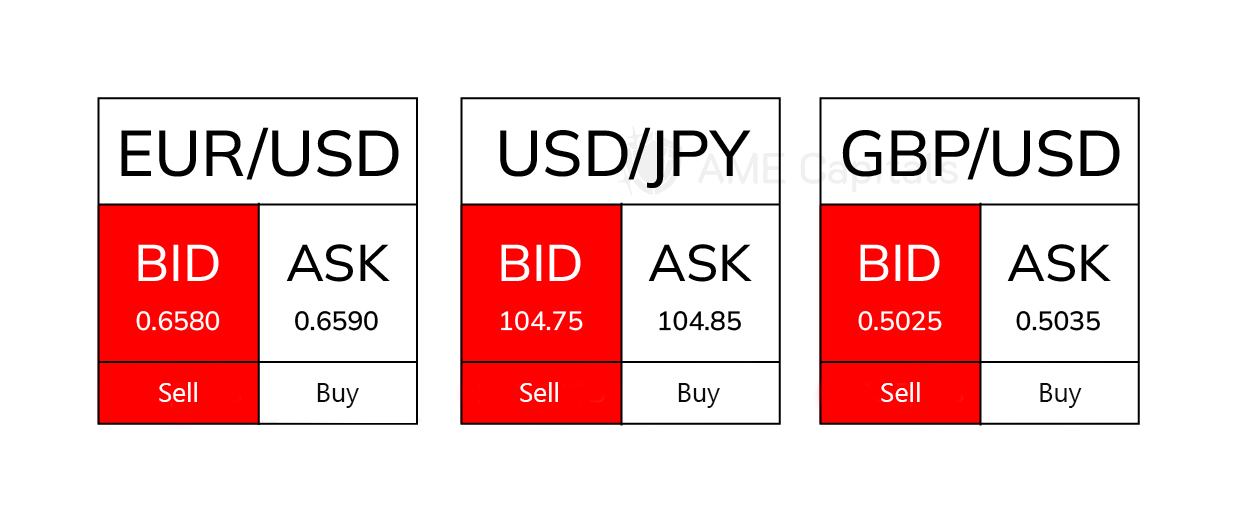
Since the big figures change slowly over time, they are often not displayed in the selling (ask) rate of official quotations in Forex. For example, the previously mentioned quotation for the US dollar against the Japanese Yen may appear as USD/JPY 104.75/85. The term "big figure" in dealer jargon refers to the base number in 100 pips, which is why only the last 2 digits are typically displayed in the selling (ask) rate of the quotation.
The difference between the selling rate and the buying rate (the right and left side of the quotation) is called the spread. The spread serves as the basis for the profit of the party providing the quotation.
Let's consider a currency exchange with a typical Forex quotation for the US dollar against the Japanese Yen, USD/JPY 104.75/85, with a spread of 10 pips. If you sell 100 US dollars, you will receive 100 x 104.75 = 10,475 Japanese Yen. If someone else comes and buys these 100 US dollars at the exchange, they will have to pay 100 x 104.85 = 10,485 Japanese Yen. Thus, the exchange earns 10,485 - 10,475 = 10 Japanese Yen. As seen from the example, the exchange earns on opposite currency transactions, i.e., when someone buys and someone sells. This principle forms the basis of brokers' profit in the Forex market.
A profit of 10 Japanese Yen (approximately 10 cents in terms of US dollars) is negligible compared to the transaction amount of 100 US dollars. That is why currency exchanges use a much larger spread than in Forex quotations, where the minimum transaction size is much larger, around 100,000 US dollars. A more realistic quotation for the exchange would be USD/JPY 102.00/108.00 with a spread of 600 pips. In that case, the profit from a 100 US dollar transaction would be 600 Japanese Yen (or 5.56 US dollars converted at the same quotation).
We will learn how to determine the profit from a transaction and convert it into the desired currency in the upcoming chapters of the website. For now, it is important to understand that in any Forex quotation, there are two rates (the buying rate and the selling rate), and the difference between these rates is called the spread, expressed in pips.
So, the spread is a source of income for the party providing the quotation. That is why retail brokerage firms, which offer individual investors the opportunity to trade on Forex through the internet, usually do not charge commissions on transactions – they earn through the spread.
In the subsequent chapters of the website, when we learn how to open and close positions on Forex, we will discuss in detail why a large spread is not advantageous for individual investors. For now, it is important to understand that when choosing an internet broker, you should pay attention to the size of the spread they offer – the smaller the spread, the better!
Currency exchange rates are determined solely by the demand and supply of currencies in the international foreign exchange market. The major active participants in the Forex market (as discussed earlier in the corresponding chapter) have the most significant influence on currency rates. By following the main trend of exchange rate movements, large passive participants and millions of smaller participants also contribute to further changes in rates. Thus, if the majority of participants are trying to sell a particular currency, its price will decrease. Conversely, if the main trend is to buy that currency, its price will rise. The trader's task is to identify these trends in a timely manner. This will be discussed in detail later in the Forex School section of the Forex Arena informational portal.
The size of the spread in quotations varies for different participants in the international foreign exchange market and at different times. For large Forex participants who engage in transactions worth millions of US dollars, the spread is minimal, usually only a few pips, as even a small spread in such transactions can generate substantial profits. For smaller Forex participants who engage in transactions with smaller amounts, the spread is larger. For example, in exchange offices, the spread can reach hundreds of pips.
In conditions of an unstable and rapidly changing exchange rate, the size of the spread can increase. During moments of buying or selling frenzy triggered by the release of important economic indicators (fundamental analysis elements will be described in detail in the Forex School section), internet brokers often widen the spread. This is also something to consider when choosing an internet broker, and it may be preferable to choose a broker with a fixed, constant spread.
The size of the spread can depend on the liquidity of a particular currency in the market. If a currency is not actively traded in the Forex market, the spread for corresponding quotations may be larger. This is especially relevant for interbank currency exchange, where banks exchange "exotic" illiquid currencies of less developed countries. Private investors, on the other hand, mainly operate in the Forex market with highly liquid currency quotations.
For large participants in the international foreign exchange market, the size of the spread may depend on the transaction amount. If the transaction amount significantly deviates from the average market amount for a particular currency, the spread may be larger. Large transactions expose the bank to significant risks, while smaller amounts increase the bank's expenses for their execution.
Ultimately, the relationship between the counterparties involved in a transaction can affect the size of the spread. If strong business relationships are established between the parties, they can come to an agreement to reduce the spread. Conversely, if a bank dealer does not wish to conduct a transaction with a particular counterparty, they may intentionally increase the spread in the quotation, effectively forcing the counterparty to decline the transaction.
Therefore, the bid price, ask price, and spread are key concepts when working in Forex. It is crucial for individual investors to have a clear understanding of these terms. Quick decisions need to be made in Forex trading, and having a solid grasp of these fundamental concepts is essential.
Individual investors should not be intimidated by the fact that Forex transactions are typically conducted in hundreds of thousands or even millions of US dollars. The principle of margin trading, which will be discussed in subsequent sections of the Forex Arena information portal, allows individual investors to engage in transactions with amounts that are hundreds of times larger than the funds they have available.






